Building an app with Angular & Firebase
August 26th, 2021 | By Jay Raj | 11 min read

Read the full tutorial about building an app with Angular and Firebase as the backend.
Provided by Google, Firebase is a service where the back end is provided as a service for use in applications. Its database (Firebase Realtime Database) is a NoSQL database where data is stored in JSON-like documents.
Setting up Firebase
Start by setting up Firebase by signing into the Firebase console. Click on the Add Project to create a new one.
You will be prompted to enter a name for your project. Our project name will be js-scrambler-demo. Next, you must enable Google Analytics for this project or not. You don't need Google Analytics since it is not required for this tutorial. Click on Create Project.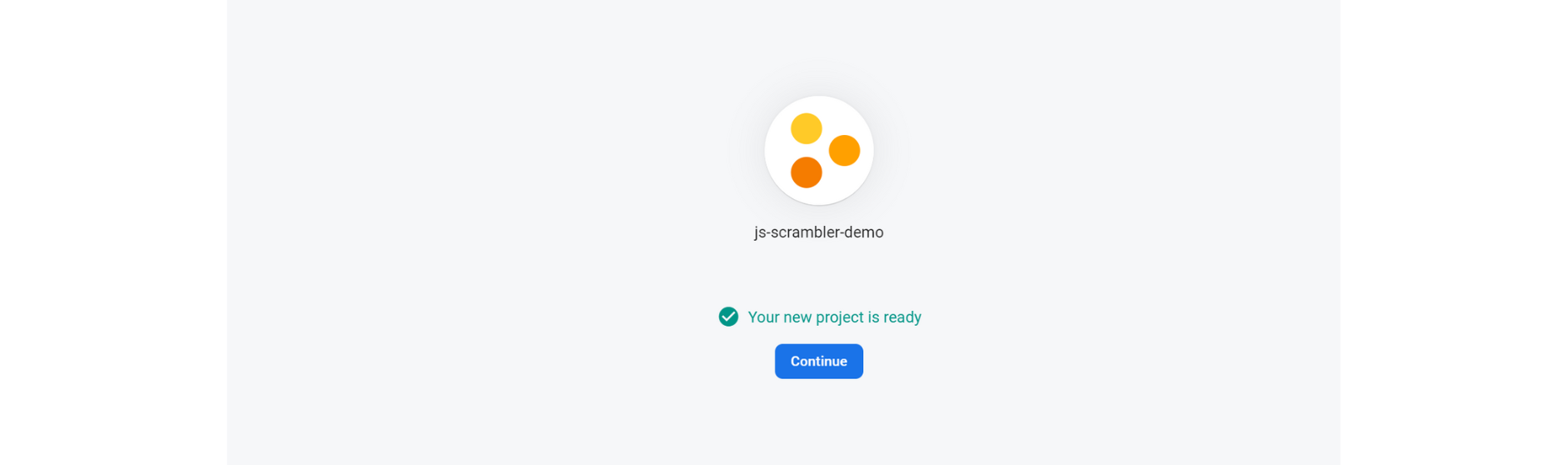
Click on the continue button, and you will be able to view the following screen:
Since we are creating a web app, click on the web icon. It asks you to register an app. Enter an app name and click on register.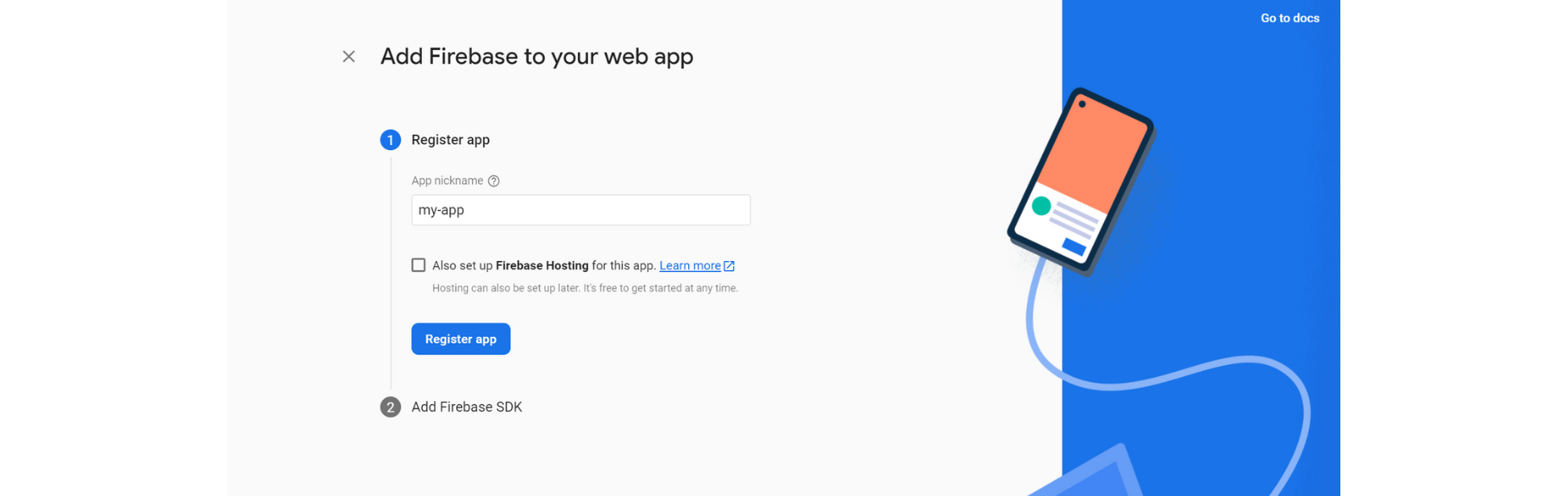
Once you click register app, you will see the Firebase app configurations.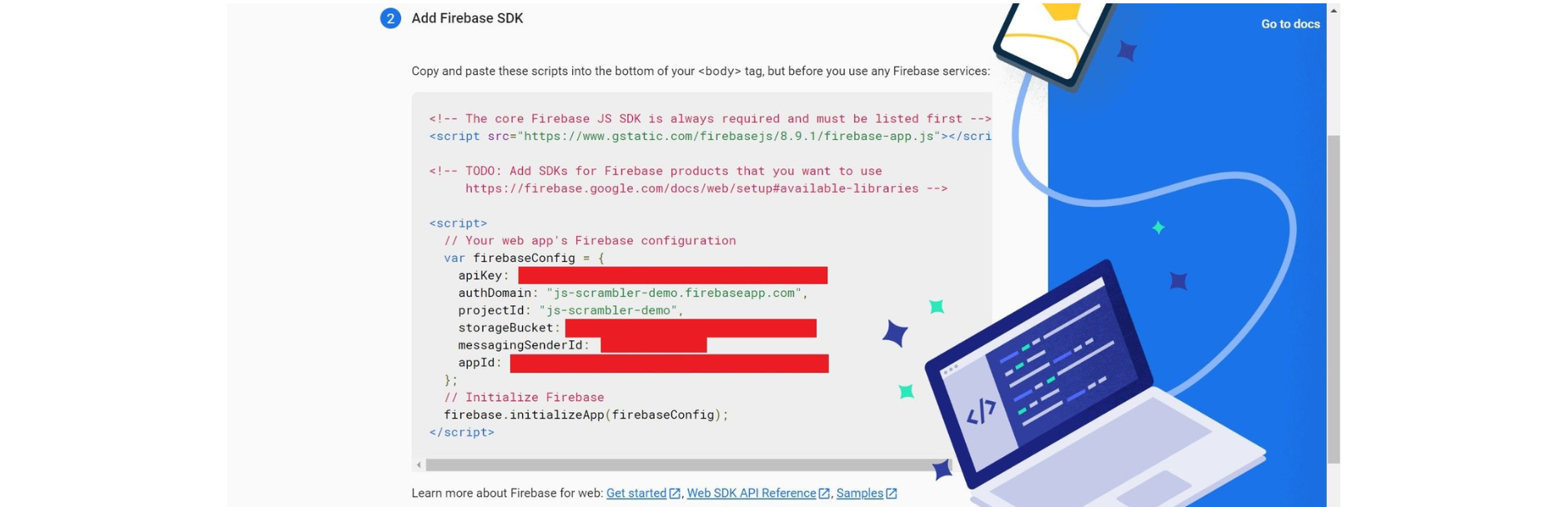
For this tutorial, we will use the above configurations in our Angular app to connect to the Firebase database. Click on the Firestore Database link from the left-side menu of the application home.
Click on the Create Database button to create a new database in Firestore. Once inside the Cloud Firestore data tab, click the Start collection button to create a new collection.
Enter the name of the collection as shown in the above screenshot. Click Next to add a new document.
We are planning to have two fields to save the name and personal information of the user, hence the fields name and personalInfo. It is time to connect Firebase to the Angular app.
Connecting Angular to Firebase
Start by creating an Angular app using the Angular CLI.
ng new angular-firebase
Install @angular/fire and Firebase to the Angular project.
npm install firebase @angular/fire
Go to your Angular app, then in the app.module.ts file, import the AngularFireModule and the AngularFirestoreModule.
import { AngularFireModule } from '@angular/fire';
import { AngularFirestoreModule } from '@angular/fire/firestore';
Using the AngularFireModule initializes the app using the configuration keys from the Firebase console. Here is how the app.module.ts file looks:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { AngularFireModule } from '@angular/fire';
import { AngularFirestoreModule } from '@angular/fire/firestore';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
AppRoutingModule,
FormsModule,
AngularFireModule.initializeApp({
apiKey: "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx",
authDomain: "js-scrambler-demo-app.firebaseapp.com",
projectId: "js-scrambler-demo-app",
storageBucket: "js-scrambler-demo-app.appspot.com",
messagingSenderId: "xxxxxxxxxx",
appId: "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
}),
AngularFirestoreModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
From the app.component.ts file, import AngularFirestore and create an instance of it in the constructor method.
import { AngularFirestore } from '@angular/fire/firestore';
constructor(private store: AngularFirestore){}
Define a method called getAll to get all the collected data from Firebase.
ngOnInit(){
this.getAll();
}
getAll(){
this.store.collection('userInfo').snapshotChanges().subscribe((response) => {
console.log('reponse ', response);
})
}
As seen in the above method, we subscribed to the collection's snapshot changes, which gives us the collection information. You can use the response to parse the collection information.
Save the above changes and run the application, and you'll be able to get the collection userInfo details in the browser console. That means we can connect to the database. Now let's see how to implement basic CRUD operations on Firebase from Angular.
Adding Bootstrap to Angular
Install Bootstrap and the required dependencies for the Angular project.
npm install bootstrap jquery popper.js
Add the following to the script references to the angular.json file under architect -> build key:
"styles": [
"src/styles.css",
"node_modules/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"
],
"scripts": [
"node_modules/jquery/dist/jquery.min.js",
"node_modules/popper.js/dist/umd/popper.min.js",
"node_modules/bootstrap/dist/js/bootstrap.min.js"
]
Fetching the Data
We fetched the data from the collection using the getAll method. But you need to parse the data and render it to the user interface.
Inside the app.component.ts file, define a variable called dataSource which we'll use to render the collection information in tabular form.
dataSource : any;
From the response received from the snapshotChanges collection, you need to iterate over each piece of data and collect the required information. You'll be requiring the unique document ID, name, and personal information from each document. Each document's payload.doc has the required information, which we can parse as shown.
getAll(){
this.store.collection('userInfo').snapshotChanges().subscribe((response) => {
this.dataSource = response.map(item =>
Object.assign({id : item.payload.doc.id}, item.payload.doc.data())
);
})
}
Now that you have the data, let's render it to the UI. For the rendering of the data, add the following HTML to app.component.html:
<div class="container m-100 main">
<div>
<svg data-bs-toggle="modal" (click)="openDialog()" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="32" height="32" fill="currentColor" class="bi bi-cloud-plus-fill" style="cursor: pointer;" viewBox="0 0 16 16">
<path d="M8 2a5.53 5.53 0 0 0-3.594 1.342c-.766.66-1.321 1.52-1.464 2.383C1.266 6.095 0 7.555 0 9.318 0 11.366 1.708 13 3.781 13h8.906C14.502 13 16 11.57 16 9.773c0-1.636-1.242-2.969-2.834-3.194C12.923 3.999 10.69 2 8 2zm.5 4v1.5H10a.5.5 0 0 1 0 1H8.5V10a.5.5 0 0 1-1 0V8.5H6a.5.5 0 0 1 0-1h1.5V6a.5.5 0 0 1 1 0z"/>
</svg>
</div>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">#</th>
<th scope="col">Name</th>
<th scope="col">Personal Info</th>
<th>
</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr *ngFor="let item of dataSource; let i = index;">
<th scope="row">{{i+1}}</th>
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>{{item.personalInfo}}</td>
<td class="action">
<svg (click)="edit(item.id)" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="16" height="16" fill="currentColor" class="bi bi-pencil-fill" viewBox="0 0 16 16">
<path d="M12.854.146a.5.5 0 0 0-.707 0L10.5 1.793 14.207 5.5l1.647-1.646a.5.5 0 0 0 0-.708l-3-3zm.646 6.061L9.793 2.5 3.293 9H3.5a.5.5 0 0 1 .5.5v.5h.5a.5.5 0 0 1 .5.5v.5h.5a.5.5 0 0 1 .5.5v.5h.5a.5.5 0 0 1 .5.5v.207l6.5-6.5zm-7.468 7.468A.5.5 0 0 1 6 13.5V13h-.5a.5.5 0 0 1-.5-.5V12h-.5a.5.5 0 0 1-.5-.5V11h-.5a.5.5 0 0 1-.5-.5V10h-.5a.499.499 0 0 1-.175-.032l-.179.178a.5.5 0 0 0-.11.168l-2 5a.5.5 0 0 0 .65.65l5-2a.5.5 0 0 0 .168-.11l.178-.178z"/>
</svg>
<svg (click)="delete(item.id)" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="16" height="16" fill="currentColor" class="bi bi-trash-fill" viewBox="0 0 16 16">
<path d="M2.5 1a1 1 0 0 0-1 1v1a1 1 0 0 0 1 1H3v9a2 2 0 0 0 2 2h6a2 2 0 0 0 2-2V4h.5a1 1 0 0 0 1-1V2a1 1 0 0 0-1-1H10a1 1 0 0 0-1-1H7a1 1 0 0 0-1 1H2.5zm3 4a.5.5 0 0 1 .5.5v7a.5.5 0 0 1-1 0v-7a.5.5 0 0 1 .5-.5zM8 5a.5.5 0 0 1 .5.5v7a.5.5 0 0 1-1 0v-7A.5.5 0 0 1 8 5zm3 .5v7a.5.5 0 0 1-1 0v-7a.5.5 0 0 1 1 0z"/>
</svg>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
As seen in the above code, we are iterating over the dataSource to render it in tabular form. Add the following CSS to the app.component.css file:
.m-100{
margin: 100px;
}
.main{
padding: 1.5rem;
border: 1px solid #dee2e6;
border-top-left-radius: .25rem;
border-top-right-radius: .25rem;
}
.action svg{
margin: 0px 5px 0px 5px;
}
Save the changes and run the Angular application. You can add some data to the collection from the Firebase console, and you should be able to see it in the Angular application.
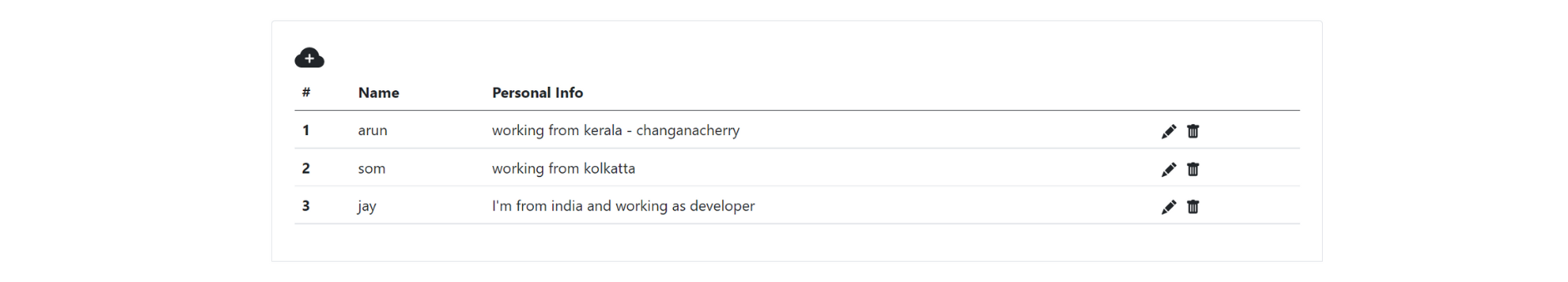
Adding New Data
In the app.component.html code, append the following HTML code to show an add/edit modal popup.
<button #btnShow style="display: none;" id="btnShow" type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-bs-toggle="modal" data-bs-target="#exampleModal" ></button>
<div id="exampleModal" #myModal class="modal" tabindex="-1">
<div class="modal-dialog">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title">Add New User</h5>
<button #btnClose id="btnClose" type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="exampleFormControlInput1" class="form-label">Name</label>
<input type="text" [(ngModel)]="name" class="form-control" id="exampleFormControlInput1" placeholder="enter name">
</div>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="exampleFormControlTextarea1" class="form-label">Personal Info</label>
<textarea class="form-control" [(ngModel)]="personalInfo" placeholder="enter some personal info" id="exampleFormControlTextarea1" rows="3"></textarea>
</div>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-bs-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" (click)="add()" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Define name and personalInfo in app.component.ts. Create a method called add that will add a new document to the userInfo collection based on the data entered in the popup.
add(){
this.store.collection('userInfo').add({name : this.name, personalInfo : this.personalInfo});
}
Inside the app.component.ts add a reference to the buttons to open and close the popup using ViewChild. Also, define two methods for opening and closing the modal popup using the button references.
@ViewChild('btnShow')
btnShow!: ElementRef;
@ViewChild('btnClose')
btnClose!: ElementRef;
openDialog(){
this.btnShow.nativeElement.click();
}
closeDialog(){
this.btnClose.nativeElement.click();
}
In the app.component.html file, you have already added a click reference to the add method. Now go ahead and also add the closeDialog method call inside the add method to close the popup after adding the document.
add(){
this.store.collection('userInfo').add({name : this.name, personalInfo : this.personalInfo});
this.closeDialog();
}
Save the changes and click on the add icon to add a new record. You will be able to add a new record from the Add New User pop-up screen.
Updating Existing Record
For updating an existing record, you need a unique document ID. So when the user clicks on the edit icon, let's keep the ID and other details in a variable.
editObj : any;
Now let's define a method called edit and pass the document ID to it. Using the ID, let's fetch the document information and populate the popup.
edit(id : string){
this.store.collection('userInfo').doc(id).get().subscribe((response) => {
this.editObj = Object.assign({id : response.id}, response.data());
this.name = this.editObj.name;
this.personalInfo = this.editObj.personalInfo;
this.openDialog();
})
}
Save the changes and click on the edit icon of any existing record, and the details will get populated.
Next, modify our add method to update an existing record.
add(){
if(this.editObj){
this.store.collection('userInfo').doc(this.editObj.id).update({name : this.name, personalInfo : this.personalInfo});
} else {
this.store.collection('userInfo').add({name : this.name, personalInfo : this.personalInfo});
}
this.closeDialog();
}
As seen in the above code, if an editObj exists, we update the particular document records, and if not, we add a new one.
Save the changes and click on the edit icon to edit an icon. Make some changes and click save. You will be able to update the existing information on Firebase.
Add a clearEdit method to clear the editObj and reset variables. You can call it by clicking the close button.
clearEdit(){
this.editObj = null;
this.name = "";
this.personalInfo = "";
}
Add the clearEdit method to the close button in app.component.html.
<button type="button" (click)="clearEdit()" class="btn btn-secondary" data
Deleting Record
For deleting a document from Firebase, you need to call the delete method on a document fetched with a document ID. Here is how the delete method looks:
delete(id : string){
this.store.collection('list').doc(id).delete();
}
The method call is already added to the app.component.htmlfile. Save the changes and click on the delete icon corresponding to a record, and you will be able to delete an existing record.
Wrapping it Up
You learned how to build a basic CRUD app using Angular and Firebase. For detailed information related to Firebase and its APIs, you can refer to the official documentation.
The source code for building an App with Angular and Firebase is available on GitHub.
Jscrambler
The leader in client-side Web security. With Jscrambler, JavaScript applications become self-defensive and capable of detecting and blocking client-side attacks like Magecart.
View All ArticlesMust read next
Integrating Firebase with React Native
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to start building your cross-platform mobile app MVP with the power of Firebase and React Native.
August 6, 2021 | By Aman Mittal | 11 min read
How To Integrate Firebase Authentication With an Expo App
In this tutorial, let's take a look at how as a mobile developer building applications using Expo SDK, you can integrate and use Firebase Authentication.
July 1, 2021 | By Aman Mittal | 14 min read
