What is Cross-Site Request Forgery?
June 23rd, 2016 | By Jscrambler | 5 min read

Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is a type of attack that occurs when a malicious website/script causes unwanted actions at a trusted service using the authentication status of logged users without their knowledge.
How it works?
The client communicates with the server with the help of GET and POST requests. The server receives data sent by the client and executes given operations.
For example, when you change your password, the GET request could look like this:
/setpassword.php?pass=12345
…and like this in POST example
/setpassword.php
$_POST['pass'] = 12345
The server sets the new password for a logged-in user. But what if the same request is sent without your knowledge through a background process or from an external service? If you’re still logged in, it will do the same! There are a few ways to achieve that.
Somebody can send you a fixed link. In this case, it would be: /setpassword.php?pass=password It can be also any other external site. The link can be run by the JavaScript. It can be even hidden inside an <img> tag through the src attribute.
<img alt="" src="http://example.com/setpassword.php?pass=passwordofhijacker"/>
The browser will try to execute/download the image. Therefore, executing the script. Because this script has a footprint on the DOM tree, Jscrambler can notify your backend server about that and you can taint user session for further analysis or even block further requests/transactions.
/setpassword.php?pass=passwordofhijacker.
Is it a POST form?
They can lure you to a website that will execute a malicious form with the same fields as at the original site. The server will treat it in the proper form. Let’s go into a more detailed example.
Example of an attack scenario
You make a lot of shopping online so you often use the website of your bank. Let’s say the form for transferring money looks like this: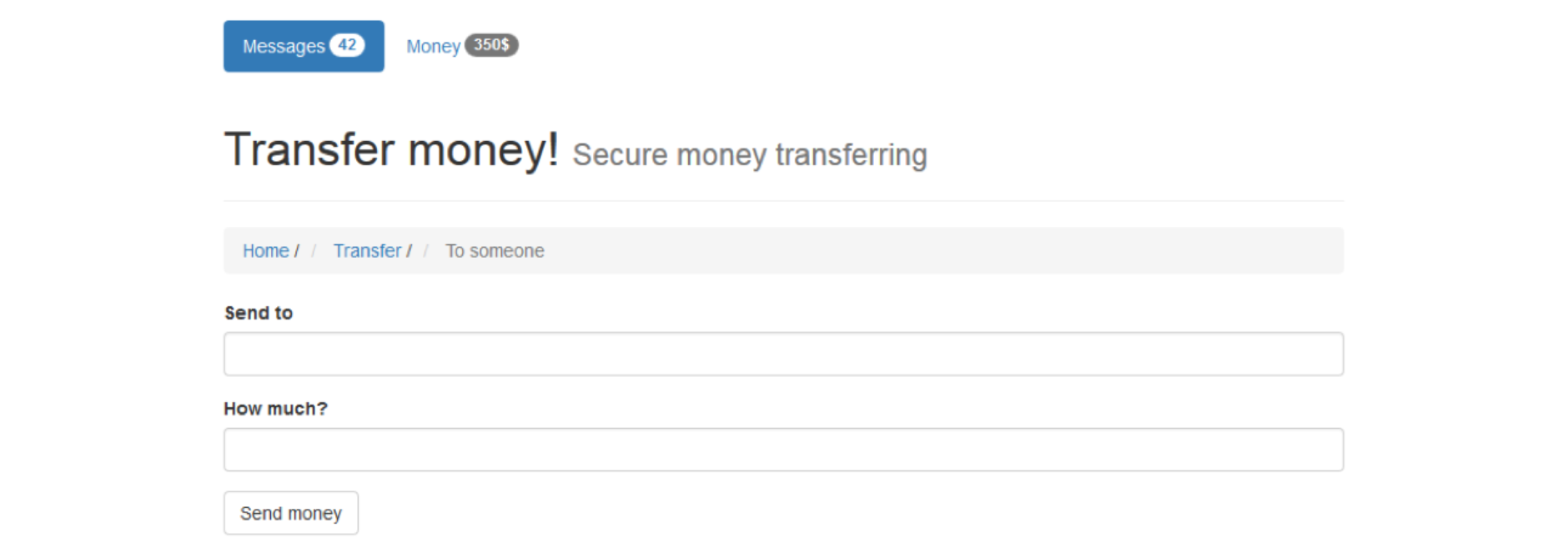 You have two important fields here.
You have two important fields here.
The number of the account you want to send money to and the value of the transfer. When you click “Send money” the form is submitted to the server. The server checks if you’re logged in and if you are, it sends the value specified in the “How much?” field to the “Send to” account. Everything is great.
But now, your friend knows that you’re a client of this bank and he’s just realized that it has a lot of security holes. He sends you a message with a link. You click it and see the photos of brand-new motorcycles.
You don’t even realize that there is a hidden form with a “Send To” and “How Much” already filled which will be automatically posted to the bank’s server. What does the server do with it?
Check if you’re logged in. You’re? Great! So money is transferred… Your friend has just received the money he spent on his purchase. So… How can you protect against it?
Ways to prevent CSRF
Checking HTTP Referrer header, origin header
It seems easy. You can do that. If a request comes from the other website you can just block it. But… What if the browser doesn’t give you this information? Or does Ads blocking or security software leave it empty? You would probably have tons of criticism from the users. And what if the attack isn’t CSRF only? It’s not so hard to spoof any header from your browser. So it’s narrow solution…
Random tokens
The easiest way to defend against CSRF is to generate random tokens. In that case server checks if the token is equal to that generated by the application before.
The attacker has no chance to know it. Unless the attacker will attack you by XSS as well… Then getting your token is not a big problem.
Double submit cookie
Another way is “double submit cookie”. We generate a random value and send it by HTTP request and cookie. The server checks if they are the same. If not, it can report a CSRF attack.
Using ready solutions
There are ready solutions to deal with this CSRF.
Anti-CSRF tools are already included in most frameworks and a lot of libraries. But… you have to remember about using them. It’s good when you generate tokens, but if you don’t validate it on the server, what’s the point in using them at all?
User interaction
Probably the best way is to extort user interaction for every operation, or at least the most important ones. It’s the safest way. What can we use? Captchamechanism, Re-authentication, or one-time tokens (sms system for example) are widely used in banking. Of course, it’s not the most convenient solution. It can be annoying to the user.
Fight with CSRF in Node.js + Express
As I said before, there are a lot of ready solutions you can use. If you’re using Node.js with Express framework, you can use csurf. It’s easy to implement and do all the dirty work instead of you.
Take a look at a simple csurf example from gitHub.
Server-side
var cookieParser = require('cookie-parser')
var csrf = require('csurf')
var bodyParser = require('body-parser')
var express = require('express')
// setup route middlewares
var csrfProtection = csrf({
cookie: true
})
var parseForm = bodyParser.urlencoded({
extended: false
})
// create express app
var app = express()
// parse cookies
// we need this because "cookie" is true in csrfProtection
app.use(cookieParser());
app.get('/form', csrfProtection, function(req, res) {
// pass the csrfToken to the view
res.render('send', {
csrfToken: req.csrfToken()
})
});
app.post('/process', parseForm, csrfProtection, function(req, res) {
res.send('data is being processed')
})
Client-side
<form action="/process" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" name="_csrf" value="{{csrfToken}}" />
Favorite color:
<input type="text" name="favoriteColor" />
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
How it Ranks in Top 10 Web Attacks
CSRF is not a well-known type of attack, but it was always quite high in the OWASP ranking.
In the 2013 ranking, it was placed at further position #8 and it seems that more and more developers remember to protect against it. It was once ignored by the web development and security communities, but now it has changed.
Recent CSRF attacks and damages
Among the victims of CSRF attacks, you can find such big brands as Digg.com, YouTube, INGDirect, MySpace, and Amazon.
In the case of digg.com, there was not so much harm, but the security hole in the shopping website allowed an attacker to change the address and buy something for himself… from the accounts of other users.
In the INGDirect case, hackers gained control of users’ accounts and they were able to transfer money! In YouTube’s case, hackers could add friends, like videos, and send messages on behalf of a hacked user.
At CVE Details you can see that developers still leave a lot of holes. Symfony 2.3.x before 2.3.35, 2.6.x before 2.6.12, and 2.7.x before 2.7.7, for instance, might allow remote attackers to have unspecified impact via a timing attack.
Limitations of the attack
CSRF attack is easy to prepare, but it’s not universal at all.
The attacker has to prepare a special script/form for a given attack. He has to know how is the website designed to make a proper request and, above all, he has to lure his victim to his malicious website. If malicious code uses JavaScript it can be also harmless due to no-script-like plugins.
Lastly, grab a copy of our free white paper about web supply chain attacks.
Jscrambler
The leader in client-side Web security. With Jscrambler, JavaScript applications become self-defensive and capable of detecting and blocking client-side attacks like Magecart.
View All ArticlesMust read next
Cross-site Scripting (XSS)
Cross-site scripting is a vulnerability that happens when there’s an injection of malicious code to run on a regular webpage.
July 1, 2022 | By David Atanda | 4 min read
Web-Based Supply Chain Attacks in the Enterprise
The enterprise is being taken by storm by web supply chain attacks, which breach them via third-party vendors. New mitigation approaches must be considered.
July 4, 2019 | By Jscrambler | 3 min read
