How To Use React Native Camera
February 7th, 2020 | By Aman Mittal | 5 min read

React Native Camera is the go-to component when creating React Native apps that require the functionality of using the device’s camera. This module has support for:
Videos
Photographs
Face Detection
Text Recognition
Barcode Scanning
It helps your React Native app communicate with the native operating system using the device's hardware by implementing some helper methods.
In this tutorial, let us build a simple QR code scanner app in React Native by implementing one of the functionalities this module supports, called Barcode scanning. We will go through the following steps:
Installing Dependicies
Setting Camera Permissions
Setting up the Camera in a React Native App
Reading QR Code Information
The complete code for this tutorial is available in this GitHub repo.
React Native Camera and React Native VisionCamera
According to GitHub, React Native Camera is now deprecated in favor of React Native VisionCamera, which offers new APIs. better performance, and much more. The first one was the perfect choice if your app required access to the device's camera to record videos or take photos.
However, let's dive into this user-friendly programming framework in general terms and the React Native Camera in a more deep way.
Can you use camera with React Native?
Consider that a React Native camera app uses your Android or iOS camera and enables you to use the package of React Native on top of it.
Step 1: Installing Dependencies
To begin, let us generate a React Native project by using the command below from a terminal window:
npx react-native init qrCodeScannerApp
# navigate inside the directory once it is generated
cd qrCodeScannerApp
Next, you have to install some dependencies to use the RNCamera module. If you are on the latest React Native version, that is, a version above 60.x.x, run the following command from a terminal window:
yarn add react-native-camera
For iOS devices, you have to install the pods as shown below:
# after dependency installation
cd ios/
pod install
cd ..
For Android users, there is no extra installation requirement at this point.
Step 2: Setting Camera Permissions
To access the device's hardware camera, a set of permissions has to be added. For iOS, please open the file ios/qrCodeScannerApp/Info.plist and add the following permissions:
<!-- Required with iOS 10 and higher -->
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>Your message to user when the camera is accessed for the first time</string>
<!-- Required with iOS 11 and higher: include this only if you are planning to use the camera roll -->
<key>NSPhotoLibraryAddUsageDescription</key>
<string>Your message to user when the photo library is accessed for the first time</string>
<!-- Include this only if you are planning to use the camera roll -->
<key>NSPhotoLibraryUsageDescription</key>
<string>Your message to user when the photo library is accessed for the first time</string>
<!-- Include this only if you are planning to use the microphone for video recording -->
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key>
<string>Your message to user when the microphone is accessed for the first time</string>
Next, to add permissions so that the app works correctly on an Android device, open the file android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml and add the following:
<!-- Required -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<!-- Include this only if you are planning to use the camera roll -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
Then, open another file android/app/build.gradle and add the following:
android {
...
defaultConfig {
...
// insert this line
missingDimensionStrategy 'react-native-camera', 'general'
}
}
That's it for the installation process for the OS platforms. In the next section, let us continue to build the app.
Step 3: Setting up the Camera in a React Native App
In this section, let us first try and test the RNCamera module.
Open the App.js file and start by adding the following import statements: Nothing fancy here. You just have to import the core React Native components such as View and Alert as well as RNCamera from react-native-camera.
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { StyleSheet, View, Alert } from 'react-native'
import { RNCamera } from 'react-native-camera'
Then, create a class component App that is going to render the JSX that uses a hardware camera on the device's screen. This is going to be done by wrapping the RNCamera component inside a View.
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<RNCamera
style={{ flex: 1, alignItems: 'center' }}
ref={ref => {
this.camera = ref
}}
/>
</View>
)
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
flexDirection: 'column',
backgroundColor: 'black'
}
})
export default App
After adding the above snippet, make sure you build the app for the OS you are using to test it. I am going to use a real Android device for testing.
# for iOS
react-native run-ios
# for Android
react-native run-android
When testing on an Android device, please make sure that the device is connected via USB and that USB debugging is enabled as well before you run the previous build command from a terminal window.
After the app has finished building and this process triggers the metro bundler, you are going to get a prompt asking for permission when the app runs for the first time.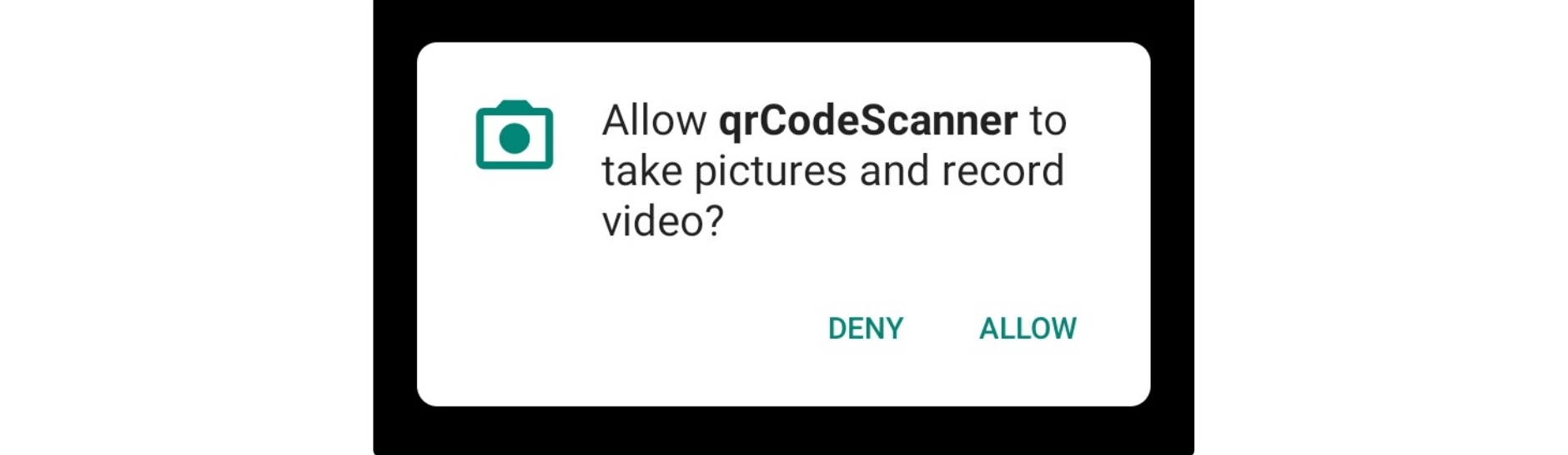
This means that the camera is working as expected, and now you can leverage this to scan QR codes.
Step 4: Reading QR Code Information
To read the QR code information, you will have to make use of the prop onGoogleVisionBarcodesDetected. This prop, with the help of a helper method, can be used to evaluate the value of the scanned QR code.
In the App.js file, start by modifying the RNCamera component as below.
<RNCamera
ref={ref => {
this.camera = ref
}}
style={styles.scanner}
onGoogleVisionBarcodesDetected={this.barcodeRecognized}
/>
Add the corresponding styles for the Camera component to the previously defined StyleSheet object.
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
flexDirection: 'column',
backgroundColor: 'black'
},
// add the following
scanner: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'flex-end',
alignItems: 'center'
}
})
Then, before the render method, add the helper method barcodeRecognized as well as the state variable barcodes, whose initial value is going to be an array.
state = {
barcodes: []
}
barcodeRecognized = ({ barcodes }) => {
barcodes.forEach(barcode => console.log(barcode.data))
this.setState({ barcodes })
}
The above helper method is going to update the state variable barcodes that can be used to render the value of the QR code scanned using the RNCamera.
Let us add two helper methods following the barcodeRecognized method. These helper methods are going to be responsible for displaying the information in the QR code.
renderBarcodes = () => (
<View>{this.state.barcodes.map(this.renderBarcode)}</View>
)
renderBarcode = ({ data }) =>
Alert.alert(
'Scanned Data',
data,
[
{
text: 'Okay',
onPress: () => console.log('Okay Pressed'),
style: 'cancel'
}
],
{ cancelable: false }
)
Lastly, to render the Alert box, make sure you add the code below to modify the RNCamera component as below.
<RNCamera
ref={ref => {
this.camera = ref
}}
style={styles.scanner}
onGoogleVisionBarcodesDetected={this.barcodeRecognized}>
{this.renderBarcodes}
</RNCamera>
That's it! Now, let us go back to the app and test it out.

Conclusion about the React Native Camera module
The react-native-camera module can be a perfect fit to leverage the device's hardware if you are building cross-platform apps with React Native.
We have only explored the barcode scanning capability, but the same principle applies if you have other goals in mind that also use the device’s camera.
Thanks to great community-built components like RNCamera, React Native apps continue to grow as great alternatives to native mobile apps, and it is mandatory to protect these apps.
Why Jscrambler's solutions to protect React Native apps?
As a final note, don't forget to pay special attention if you're developing commercial or enterprise React Native apps that contain sensitive logic.
You can protect them against code theft, tampering, and reverse engineering.
Speak with our client-side security experts or request a demo to explore our solutions for JavaScript in-app protection and real-time webpage monitoring.
Jscrambler
The leader in client-side Web security. With Jscrambler, JavaScript applications become self-defensive and capable of detecting and blocking client-side attacks like Magecart.
View All ArticlesMust read next
Build a Chat App with Firebase and React Native
In this tutorial, let's build a mobile chat application using React Native, Expo and Firebase - a great way to evolve your JavaScript skills.
November 26, 2021 | By Aman Mittal | 13 min read
From React to React Native in 30 Minutes
Learn how to make a iOS app, using React Native, in 30 minutes
September 2, 2015 | By José Magalhães | 5 min read
Getting Started with VR in React Native with ViroReact
By the end of this tutorial, you will have created a simple VR cross-platform mobile application using React Native and ViroReact.
February 19, 2019 | By Wern Ancheta | 9 min read
